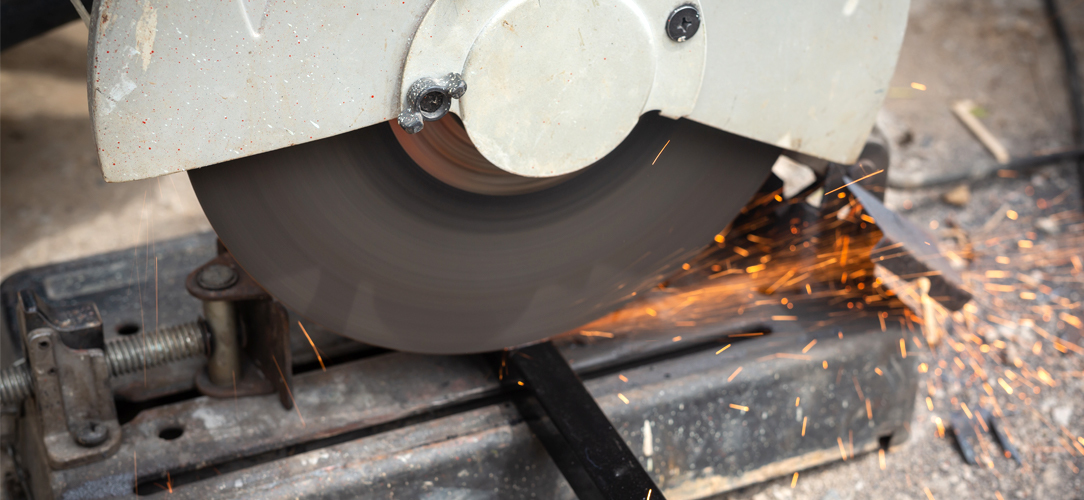
Guide to Circular Saws for Cutting UPVC & Aluminium
Celebrated for their durability, versatility, and aesthetic appeal, UPVC and aluminium are materials that are essential for a wide range of applications — from the sleek lines of automotive parts to the sturdy yet elegant frames of windows and doors.
As industries continuously evolve, the need for precise, clean, and efficient cutting solutions for UPVC and aluminium becomes ever more critical. To meet these needs, circular saws have evolved to become essential pieces of equipment for a variety of businesses. The versatility of these saws, when armed with the correct blades and techniques, makes them indispensable.
The precision cuts, speed, and adaptability offered by circular saws align perfectly with the demands of modern manufacturing and construction projects, where time is of the essence, and quality is non-negotiable.
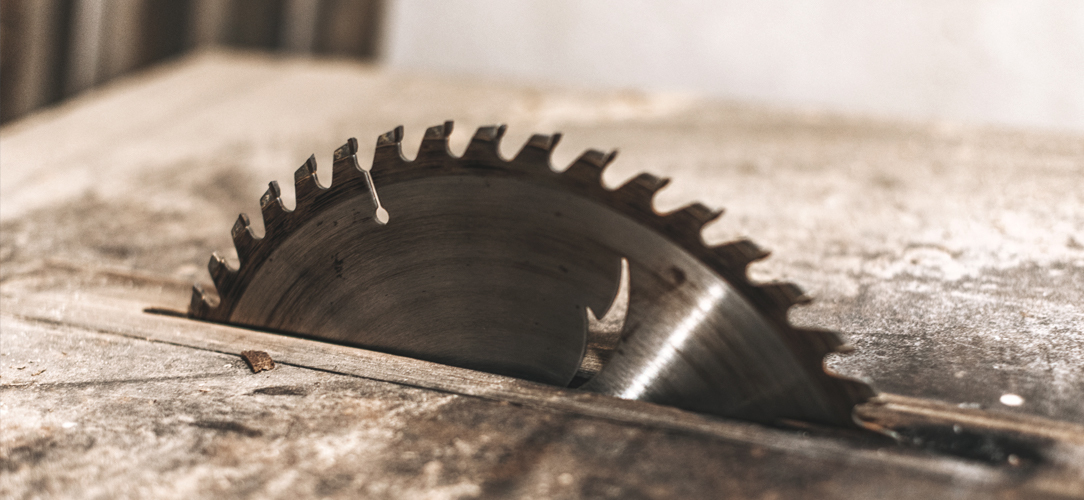

ClUnderstanding Circular Saws
A circular saw is a versatile tool in commercial manufacturing, offering precision and efficiency. There are various types of circular saws available, each suited for different applications.
Table and pedestal mounted circular saws are a staple in professional and industrial environments, such as workshops and fabrication businesses. These saws are designed for heavy-duty applications, offering precision and consistency crucial for commercial-grade manufacturing.
Circular saws offer a range of benefits that apply to cutting materials such as UPVC and aluminium, including:
Sturdy Construction & Stability
Industrial circular saws are constructed with heavy-duty materials for maximum stability and minimal vibration. This robust build ensures accurate and consistent cuts, essential in precision manufacturing.
Power & Performance
Equipped with high-power motors, often three-phase, these saws can handle prolonged use and efficiently cut through thick materials. The substantial power output meets the demands of industrial tasks, ensuring efficiency and reliability.
Precision & Accuracy
These saws typically feature advanced alignment systems and calibrated scales, allowing for highly accurate cuts. Fine adjustments for blade angle and height enable complex cuts and detailed joinery, crucial for precision fabrication.
Advanced Cooling Systems
Integral cooling systems, using mist or liquid coolant, prevent overheating – a critical factor when cutting materials like aluminium. This feature extends blade life and enhances cut quality, maintaining efficiency in prolonged operations.
Heavy-Duty Blade Design
Blades are generally large in diameter, often made of carbide-tipped or high-speed steel, tailored for durability and precision.
Specialised teeth are designed to effectively cut through the varying hardness of aluminium and the softness of UPVC without damaging the material.
Precision Cutting & Mitre Capability
The saws enable precise straight and mitre cuts at a range of angles.
Some models offer programmable angles and automated adjustments, ideal for repetitive and precision cutting in commercial settings.
Clamping & Material Handling
Equipped with pneumatic or hydraulic clamps, these saws securely hold materials during cutting.
Additional features like conveyor systems or material supports aid in handling larger profiles, streamlining the workflow.
Safety Features
Safety features such as blade guards, riving knives, and emergency stop mechanisms come as standard in these saws. They also comply with industrial safety standards, ensuring operator safety, and can also be fitted with options such as extraction and dust collection systems.
Extended Work Area And Material Support
The saws provide a substantial work surface, with options to add extensions and supports for larger materials.
This adaptability is crucial in commercial applications where handling diverse material sizes is common.
Ease Of Maintenance And Upkeep
Designed for continuous operation, these saws are built for straightforward maintenance.
Easy access to parts for cleaning and blade replacement is a key design consideration, ensuring longevity and consistent performance
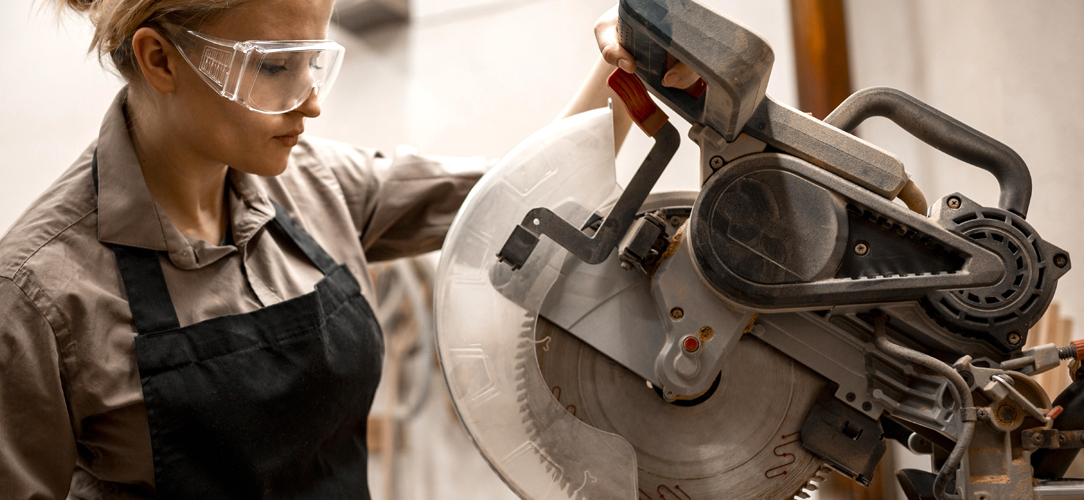

Applications Of Circular Saws For Cutting UPVC & Aluminium
A wide range of businesses rely on circular saws on a daily basis. When used for cutting aluminium or UPVC, applications commonly include:
Window & Door Manufacturing: UPVC is commonly used for window and door frames due to its durability and low maintenance. Circular saws are used to cut these profiles to size with accuracy and a high-quality finish.
Construction & Building: Aluminium is often used in building facades, roofing, and structural components. Circular saws ensure precise cuts for fitting and assembly in construction projects.
Automotive & Aerospace Parts: In industries where aluminium is used for its lightweight yet strong properties, like in automotive or aerospace manufacturing, circular saws are essential for cutting parts to exact specifications.
Furniture & Cabinetry: UPVC is sometimes used in furniture and cabinetry for its moisture resistance. Circular saws can be used to cut panels and profiles for these applications.
Signage & Decorative Elements: For cutting aluminium or UPVC sheets used in signage, displays, or decorative elements, circular saws provide the necessary precision and clean edges.
Electrical Conduits & Piping: In electrical installations, UPVC conduits and piping need to be cut to length, and circular saws offer a quick and accurate method to do this.
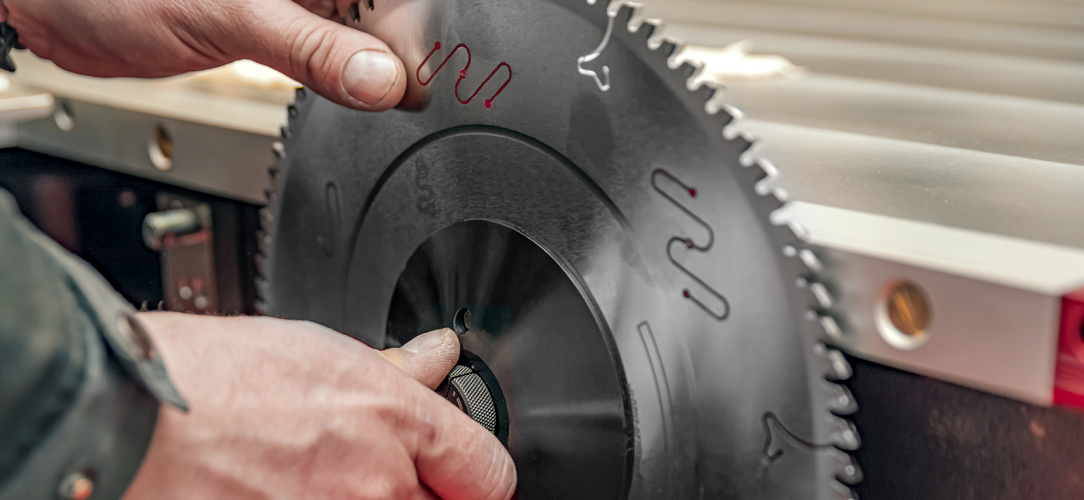

Types Of Circular Saws & Chop Saws
Circular saws come in various types, each with unique features and applications.
Manual Circular Saws
Manual circular saws are the most straightforward, requiring physical intervention by the operator for most actions. The operator needs to manually guide the saw through the material and lift the saw head after each cut.
Good quality manual saws offer high levels of performance, however they do not offer the same level of features as more sophisticated machines which means they are generally less expensive than their semi-automatic and automatic counterparts.
Manual circular saws are typically best suited for jobs that involve smaller diameters of materials, for operations that require less frequent sawing, or for workshops where space is at a premium.
Semi-Automatic Circular Saws
Semi-automatic saws use hydraulic pistons to raise and lower the saw head, reducing the physical strain on the operator. These saws can perform several tasks automatically, like clamping the material, starting the blade, and controlling the coolant flow. They also offer enhanced levels of safety as their design means that the cutting is fully enclosed by a lid.
An air-over-oil feed system allows for complete control of the feed rate, improving accuracy and extending blade life. Semi-automatic circular saws come in different configurations including straight cut, double miter, or compound cut saws, with varying saw motor power and blade sizes.
Semi-automated machines are well suited to operations that require higher levels of cutting to be carried out or need to chop larger diameter materials.
Automatic Circular Saws
Fully automatic saws can operate continuously without the need for operator intervention after setup. These saws are equipped with vices for material advancement, and can feature shuttle vices or powered roller vices for efficient material positioning.
Designed for high-volume cutting, they can store multiple-step programs and optimise processing via user-friendly controls and sensors. Automatic saws offer a range of features like servo-controlled saw head rotation, built-in automatic pusher systems, and hydraulic control of feed rates. They can handle various cut types, including straight, miter, and compound cuts, with a range of blade diameters available.
Each type of circular saw is designed to cater to specific needs in a fabrication or manufacturing setting. Manual saws are ideal for smaller, less frequent jobs or where portability is essential. Semi-automatic saws strike a balance between manual effort and automation, suitable for varied applications with a focus on precision and operator comfort. Fully automatic saws are tailored for high-volume, repetitive tasks where efficiency and consistency are paramount.
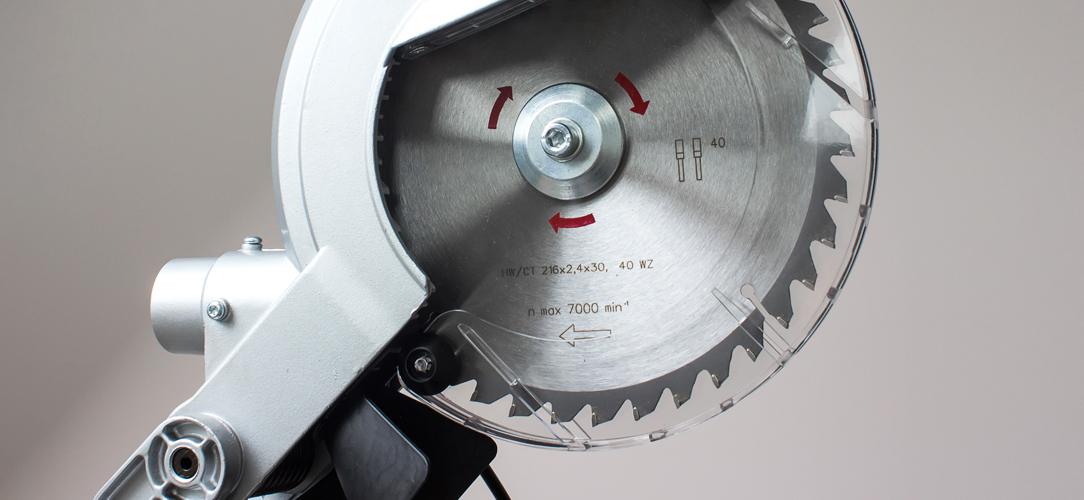

Blades For UPVC And Aluminium Cutting
Circular saw blades designed for UPVC and aluminium have specific characteristics. These include a high tooth count for smooth cuts, carbide or diamond-tipped teeth for durability, and a design that minimises material melting. The blade size will depend on the saw type and the thickness of the material to be cut.
Circular Saw Blades For Cutting UPVC
Tooth Material and Configuration: For UPVC, blades made from carbide or tungsten carbide are ideal due to their durability and resistance to wear. The teeth should have a triple-chip grind (TCG) design, which combines a raker tooth with alternating chamfered teeth, effectively reducing chipping.
Tooth Count: High tooth count blades are preferable for UPVC. A higher tooth count results in finer, smoother cuts with less risk of chipping or melting the material. Typically, a blade with 80 to 100 teeth would be suitable for most UPVC cutting tasks.
Blade Diameter and Kerf: The diameter of the blade should match the saw's specifications and the material thickness. A thinner kerf (the width of the cut the blade makes) is beneficial as it reduces material waste and requires less power to cut through the UPVC.
Hook Angle: The hook angle or rake angle of the teeth should be low to neutral. This ensures a smoother entry of the blade into the material, minimising grabbing or aggressive cutting, which can be detrimental to UPVC.
Circular Saw Blades For Cutting Aluminium
Blade Material: Blades designed for aluminium usually feature carbide tips as well, which withstand the rigidity of the metal. Some blades may also use special coatings to reduce friction and heat buildup.
Tooth Design: The TCG tooth design is also effective for aluminium, as it can handle the metal's toughness while providing a smooth finish. The chamfered teeth alternate with raker teeth to efficiently eject chips and reduce material buildup on the blade.
Tooth Count and Gullet Size: Blades for aluminium typically have fewer teeth than those for UPVC, usually ranging from 60 to 80 teeth, depending on the thickness and type of aluminium. Larger gullets between teeth help in chip removal, preventing clogging and overheating.
Blade Diameter and Kerf: Similar to UPVC, the blade diameter should be compatible with the saw and the material. A blade with a moderate to thin kerf is preferable for aluminium to ensure precise cuts and reduce material wastage.
Hook Angle: A negative to low hook angle is generally best for aluminium to prevent the blade from feeding too aggressively into the material, which can cause the saw to kick back or the material to clamp onto the blade.

Material Characteristics, Handling & Cutting Tips
UPVC is a versatile, lightweight plastic material commonly used in window frames and piping. It's known for its durability, resistance to chemicals, and low maintenance. However, UPVC can be sensitive to temperature changes, leading to expansion or contraction. Its low melting point also makes it prone to deformation under high heat generated during cutting.
Aluminium is favoured for its strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and ductility. It's a soft, malleable metal that's easy to cut and shape, making it ideal for a range of applications from construction to automotive. Aluminium's high thermal conductivity means it can quickly transfer heat, which can affect cutting if not properly managed, whether using circular saws or aluminium-cutting bandsaws.
Handling And Preparation
When handling UPVC, it's important to avoid scratches and surface damage. Use soft supports or padding when clamping UPVC materials. Due to its tendency to expand or contract with temperature changes, ensure the material is acclimatised to the workshop environment before cutting.
Aluminium, though strong, can bend or warp if not supported adequately. Ensure that the material is properly secured and supported along its length, especially when making long cuts. Remove any protective film only in the area of the cut to prevent marking the rest of the material.
Cutting Preparation
For both UPVC and aluminium, consider the ambient temperature and material temperature. For UPVC, extreme cold can make it brittle, while heat can soften it too much. Aluminium should be cut at a moderate temperature to prevent blade gumming and material warping.
Clean the surface of both materials before cutting to ensure there’s no debris that can cause blade deflection or affect the cut's precision. For aluminium, removing any oxidised layers or coatings is crucial for a clean cut.
Clamping And Stability
When cutting aluminium and UPVC in fabrication environments, both materials require secure clamping to prevent movement during cutting. However, avoid over tightening clamps on UPVC to prevent indentation or cracking.
Use roller tables or support stands for long pieces of aluminium to maintain stability during the cut. For UPVC, specialised clamps that distribute pressure evenly can prevent material distortion.
Minimising Material Waste
Plan cuts to maximise material usage and minimise waste. For UPVC, consider the expansion factor in sizing. For aluminium, use nesting techniques where possible to get the most out of each sheet or profile.
Both UPVC and aluminium offcuts can often be recycled. Set up a system for collecting and sorting these materials to reduce waste and contribute to sustainable practices.
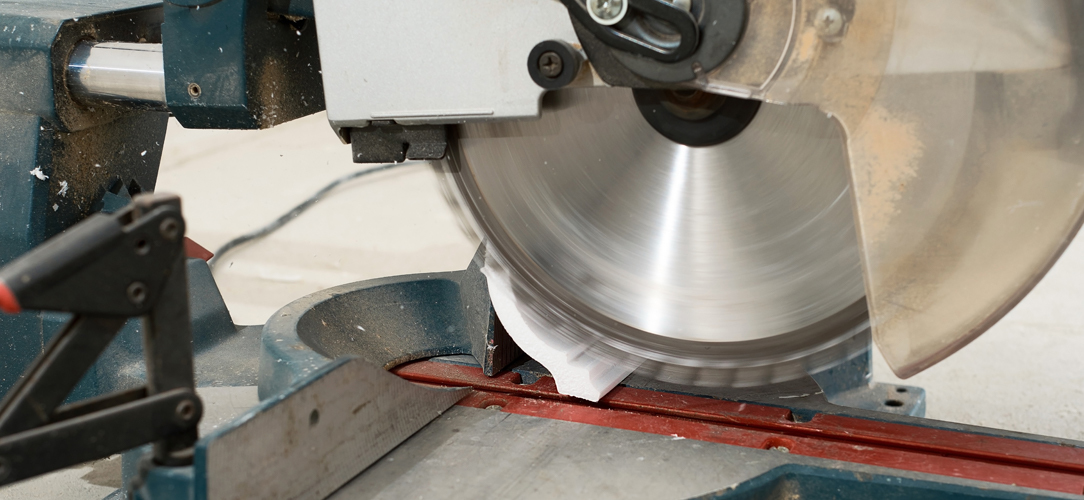

Cutting Techniques & Best Practices
When cutting materials such as UPVC or aluminium profiles using a circular saw, there are some specific techniques to be aware of to ensure precision and finish quality.
Before each cut, inspect the blade for damage or dullness, and ensure the material is free from defects or foreign objects. Always wear appropriate safety gear, including eye protection, ear protection, and a dust mask, especially when cutting materials like UPVC that can produce harmful particles.
Keep the work area clean and well-lit. A cluttered area can lead to accidents or interfere with the precision of the cut. Accurately measure and mark your cutting line. A precise cut starts with accurate measurements. Use a sharp pencil or fine marker for clear, thin lines. After cutting, inspect the material for any imperfections. If the cut is not as expected, adjust the saw settings or blade before proceeding with more cuts.
For UPVC Cutting
Gradual Feed Rate: UPVC is prone to melting if cut too quickly due to frictional heat. Use a slow, steady feed rate to prevent the material from melting and sticking to the blade.
Blade Height Adjustment: Set the blade height so that it's just above the thickness of the UPVC. This reduces the contact area between the blade and material, minimising heat build-up.
Supporting the Material: Use supports on either side of the cut to prevent the material from bending or vibrating. This is crucial for long or thin UPVC profiles.
Using a Guide or Fence: A guide or fence ensures straight cuts and helps maintain a consistent angle, particularly important for joinery work in UPVC.
For Aluminium Cutting
Lubrication: Applying a cutting lubricant can help reduce heat and prolong blade life. Some blades are designed to be used dry, so check the manufacturer's recommendations first.
Clamping: Securely clamp the aluminium to prevent it from moving during cutting. Vibration or movement can lead to rough cuts or blade binding.
Blade Speed: A higher blade speed is generally more effective for cutting aluminium, but this needs to be balanced with the feed rate to avoid excessive heat.
Chip Clearance: Ensure chips are cleared away efficiently. Excess chips can get re-cut by the blade, causing unnecessary wear and poor cut quality.
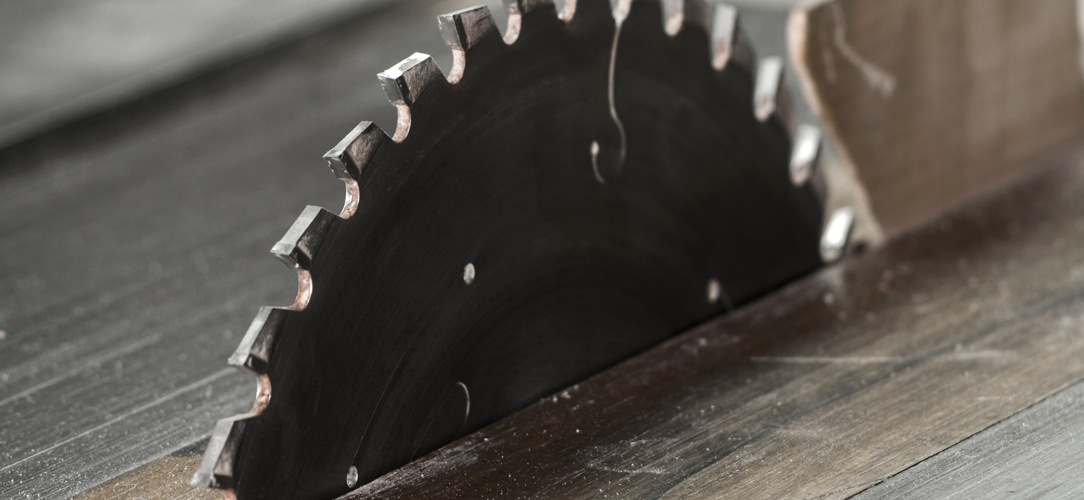

Maintenance And Care Of Blades
As with bandsaw blades, taking good care of circular saw blades is essential for safety, performance and efficiency.
Conduct regular inspections of your blades for signs of wear, dullness, or damage. Look for chipped teeth, warping, or any deformities. A compromised blade can not only affect cut quality but also pose a safety risk.
After each use, clean the blade to remove any accumulated debris, resin, or aluminium chips. Use a specialised blade cleaner or a mild detergent and a soft brush to gently clean the teeth and the blade body. Avoid using harsh chemicals that can damage the blade.
Using a worn-out blade can be inefficient and dangerous, and reduce the quality of your cuts. Blades with dull teeth require more force to cut and can generate excessive heat. Good quality blades will offer good performance, and particularly if the blade is carbide-tipped, should provide a long life. However, it is always recommended to replace blades that show signs of significant wear or damage.
Store blades in a dry, safe place where they are not at risk of being knocked or damaged. Hanging blades on a wall rack or storing them in original packaging or blade cases is ideal. This prevents the teeth from getting chipped or the blade from bending. Handle blades carefully to prevent accidental drops or impacts. Even a small chip on a carbide tooth can render the blade less effective.
Apply a light lubricant on the blade, especially if it’s not going to be used for an extended period. This helps in keeping it free from rust and corrosion. Be sure to use a lubricant that is safe for saw blades and does not attract dust. In humid environments, blades can develop rust. Using silica gel packets or rust inhibitors in storage areas can help prevent moisture buildup. If rust does appear, gently remove it with a suitable rust remover and a soft cloth, ensuring not to damage the teeth.
Keep a log of maintenance activities for each blade. Record sharpening dates, cleaning routines, and any noticeable wear or damage. This helps in tracking the blade’s condition over time and making informed decisions about sharpening or replacement.

Material Cutting Workflow Optimisation
Circular saws are essential pieces of equipment in a range of sectors. Whether a saw is being used to cut UPVC, aluminium or other materials, it is worth taking the time to plan how the machine will integrate into the workflow of your operation.
Efficient Layout And Setup
Arrange the circular saw and associated equipment in a manner that optimises the flow of materials. Consider the sequence of operations and position equipment to minimise unnecessary movements. This includes the placement of material storage, cutting area, and assembly or finishing stations.
Design the workspace to reduce strain on the operator. Adjust the height of worktables and saws to a comfortable level. Use anti-fatigue mats where operators stand for long periods.
Organise tools and accessories for easy access. Use tool boards, shadow boards, or dedicated drawers to store blades, wrenches, safety gear, and measurement tools. This minimises downtime spent searching for tools.
Material Handling & Storage
Implement a clear system for material in-feed and out-feed. Use roller conveyors or feed tables for easy movement of large or heavy materials. Clearly mark areas for raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished products.
Store materials, especially large sheets or lengthy profiles, in a way that prevents damage and allows easy retrieval. Vertical storage racks for sheet materials and horizontal racks for profiles can save space and reduce handling time.
Cutting Process Streamlining
When multiple pieces require similar cuts, batch processing can significantly increase efficiency. This reduces the frequency of adjustments to the saw and can optimise material usage.
Use jigs or templates for repetitive cuts. This ensures consistency and speeds up the process, especially for complex shapes or angles.
Dust & Waste Management
Implement efficient dust and chip extraction systems to keep the cutting area clean and reduce the time spent on cleanup. This is particularly important for UPVC cutting, which can generate a significant amount of dust.
Set up bins or areas for segregating waste materials. Recycle offcuts or scrap where possible, and ensure proper disposal of non-recyclable waste.

Health & Safety Considerations
Circular saws are incredibly useful for cutting materials such as UPVC and aluminium, and are widely used in industries such as manufacturing and fabrication of doors, windows and other construction components.
While these machines are designed with operator safety in mind, it’s important to be aware of a range of workplace safety considerations in order to maintain the welfare of personnel.
Safe Operation Of Equipment
Equipment Training: Ensure all operators are properly trained in using circular saws, including understanding different materials' cutting techniques.
Pre-use Checks: Perform routine checks before using the saw, including inspecting the blade for damage, ensuring all guards are in place, and checking the saw's stability.
Proper Use of Controls: Familiarise operators with all controls and emergency stops. Stress the importance of never bypassing safety features.
Safe Material Handling: Train staff in safe handling techniques for UPVC and aluminium to prevent injuries from sharp edges or heavy lifting.
Work Environment Safety
Adequate Ventilation: Ensure good ventilation in the workspace, particularly important when cutting UPVC, which can release harmful fumes when heated.
Cleanliness and Order: Maintain a clean, organised work area to minimise the risk of accidents. Regularly remove sawdust, offcuts, and other debris.
Lighting & Visibility: Provide sufficient lighting in the cutting area for clear visibility, reducing the risk of mistakes and accidents. Ensure all necessary signage is suitably placed and visible.
Emergency Procedures
First Aid Training: Ensure staff are trained in basic first aid to deal with common injuries like cuts or exposure to harmful substances.
Emergency Plan: Have a clear emergency plan in place for different scenarios, including accidents involving the saw or exposure to hazardous materials.
Fire Safety: Because UPVC and aluminium can ignite under certain conditions, ensure fire extinguishers are accessible and staff are trained in their use.
Regular Maintenance And Inspections
Scheduled Maintenance: Regularly service and maintain equipment to prevent malfunctions that could lead to safety incidents.
Safety Inspections: Conduct periodic safety inspections to identify potential hazards in the work environment, such as loose cables, unstable work surfaces, or improper storage of materials.
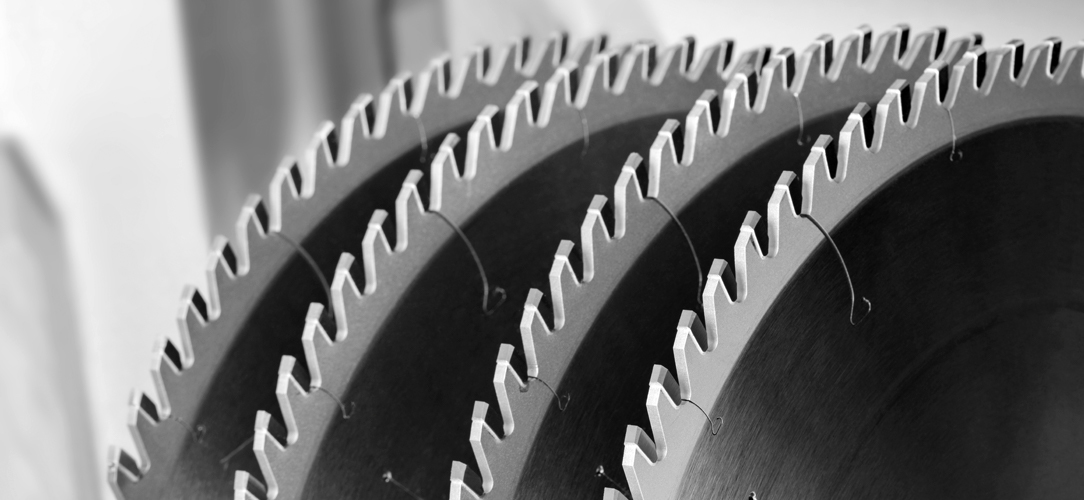

Find The Ideal Cutting Solutions For Your Operation
Circular saws are highly efficient tools for cutting UPVC and aluminium, offering precision, versatility, and speed. Their ability to make quick, clean, and accurate cuts makes them indispensable in industries ranging from construction and manufacturing to automotive and aerospace.
The choice of the right circular saw and blade is crucial for achieving the best results in cutting these materials, ensuring quality in the final products.
At Saws UK our team has decades of experience in supplying circular saws and bandsaws to businesses in a broad range of sectors. From sourcing the best machine for your requirements, to finding the best blades and replacement parts for your needs, we’re able to offer expert advice on all aspects of professional cutting and sawing. We also offer a range of professional services including training, commissioning and servicing.
For information, advice or assistance, contact our team today to discuss your requirements and find out more about what we can offer.
Share this post: